If you’ve ever heard whispers about “blue waffle disease,” you’re not alone. This mysterious term has circulated online and in school hallways, often described as a terrifying sexually transmitted infection (STI) that supposedly turns the vagina blue. But is blue waffle disease real, or is it just another internet hoax? Let’s dive into the facts, debunk the myths, and explore the real STDs you should be aware of.
What Is Blue Waffle Disease?
The term “blue waffle” first emerged in the early 2000s as an internet prank. It originated from a shock website called “bluewaffle.net,” which featured a heavily edited image of a discolored, infected vagina. The site claimed this was a real STD called “blue waffle disease.” The image, combined with the shocking name, quickly went viral, sparking fear and curiosity.
Despite its graphic nature, blue waffle disease is not a real medical condition. It was created as a joke to shock and mislead people. However, the hoax gained traction, and many began to believe it was a genuine health concern. In 2013, a New Jersey councilwoman even publicly claimed that blue waffle disease had caused deaths in her community, further fueling the myth.
How Did the Blue Waffle Hoax Go Viral?
The spread of the Blue Waffle hoax was fueled by a deceptive yet effective bait-and-switch tactic. The prank’s creators circulated images of blue-tinted waffles with captions such as, “Bet you can’t find me on Google Image search!” This strategy piqued curiosity, prompting users to search for “blue waffle.” However, instead of breakfast food, they were confronted with a disturbing and graphic image falsely claimed to depict a severe sexually transmitted infection (STI).
This viral marketing technique not only tricked unsuspecting internet users but also contributed to widespread misinformation. The shocking nature of the image led to social media discussions, online debates, and fear-based sharing, further amplifying the hoax’s reach. Over time, various websites and forums added fuel to the fire by reinforcing the myth, falsely associating Blue Waffle with real medical conditions.
Other Variations of Internet Shock Sites
As the Blue Waffle meme gained notoriety, several similar shock sites emerged, aiming to exploit its viral status. These websites typically featured disturbing or grotesque images alongside misleading descriptions. The original Blue Waffle image was first uploaded to Documenting Reality, showing a yeast infection treated with crystal violet, an antibacterial dye. Inspired by its success, other hoax-based shock sites soon followed, each designed to startle and disgust viewers.
- Red Pancake: This variation displayed an image of an inflamed anus, possibly affected by anal warts or an HPV infection.
- Giant Cheese Taco: Featured a highly graphic depiction of an ulcerated, infected vagina covered in yellow pus and blood.
- Genetic Waffle: First appearing in late 2011, this site showcased a pornographic image of a vagina suffering from prolapse or vulvitis. Created by Heyya.org, its name and content were directly inspired by the Blue Waffle meme. Like many other shock sites, Genetic Waffle was eventually taken down.
Although these shock sites gained temporary attention, most of them have since been removed from the internet. However, the legacy of the Blue Waffle hoax continues to resurface periodically, reminding users to fact-check viral claims before spreading misinformation.
Why Did People Believe the Blue Waffle Myth?
The blue waffle hoax succeeded because it preyed on people’s fears and lack of sexual health education. Many individuals, especially young people, turned to the internet for answers about STDs. Without access to reliable information, they were vulnerable to misinformation.
Additionally, the graphic nature of the images made the hoax seem more credible. People assumed that such a shocking visual must be based on reality. This highlights the importance of critical thinking and verifying information from trusted sources.
Real STDs You Should Know About
While blue waffle disease is fake, there are many real STDs that pose serious health risks. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 1 in 5 Americans has an STI on any given day. Here are some of the most common STDs and their symptoms:
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis and is the most common curable STD. Many people with chlamydia experience no symptoms, but it can cause vaginal or penile discharge, burning during urination, and pelvic pain. If left untreated, it can lead to infertility and other complications.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, also known as “the clap,” is caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Symptoms include painful urination, abnormal discharge, and, in some cases, rectal bleeding. Antibiotic-resistant strains of gonorrhea are becoming more common, making treatment more challenging.
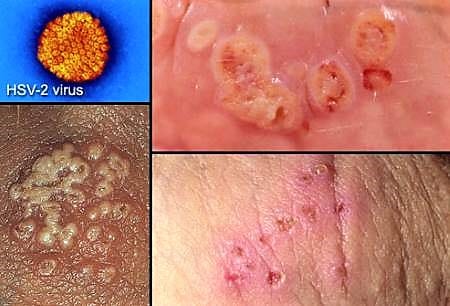
Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). While some people experience no symptoms, others may develop painful blisters or sores in the genital area. There is no cure for herpes, but antiviral medications can help manage symptoms.
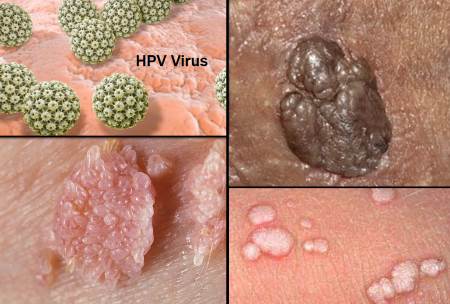
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
HPV is the most common STI in the United States, with over 200 known strains. Some strains cause genital warts, while others can lead to cervical, anal, or throat cancer. The HPV vaccine is highly effective in preventing infection.
Syphilis
Syphilis is a bacterial infection that progresses in stages. Early symptoms include sores and rashes, but if left untreated, it can cause severe damage to the heart, brain, and other organs. Syphilis is curable with antibiotics.
How to Protect Yourself from STDs
While blue waffle disease is a myth, the importance of protecting yourself from real STDs cannot be overstated. Here are some key steps to reduce your risk:
- Use condoms or dental dams during sexual activity.
- Get tested regularly, especially if you have multiple partners.
- Communicate openly with your partner(s) about sexual health.
- Consider vaccinations, such as the HPV vaccine.
- Avoid sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia.
Combating Misinformation: The Importance of Reliable Sexual Health Resources
Accurate and trustworthy information about sexual health is essential for preventing sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and promoting overall well-being. Misinformation, on the other hand, can create unnecessary fear, lead to poor decision-making, and even contribute to the stigma surrounding sexual health. To make informed choices, it’s important to rely on credible sources such as healthcare providers, official public health organizations, and reputable educational institutions.
Why Reliable Information Matters
The blue waffle myth is a prime example of how misinformation can spread rapidly, causing confusion and alarm. This hoax highlights the critical need for improved sexual health education and the widespread dissemination of accurate information. With the rise of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), which can create realistic but fake images and videos, the spread of false information has become even more challenging to control. This makes it all the more important for educators, healthcare professionals, and public health advocates to provide clear, factual, and accessible information about sexual health. Debunking myths and addressing misinformation directly are key steps in this process.
Social media platforms like TikTok, Twitter, and Instagram often amplify misinformation, as sensational content tends to go viral quickly. This is why it’s crucial to approach online information with a critical eye and verify facts before accepting them as true.
How to Identify Trustworthy Sources
With so much information available online, it can be difficult to distinguish between reliable sources and misleading content. Here are some tips to help you identify trustworthy sexual health information:
- Check the Credentials: Reliable sources are often backed by recognized medical institutions, public health organizations, or certified healthcare professionals. Look for author credentials or organizational affiliations.
- Look for Citations: Trustworthy articles and resources typically cite their sources, allowing you to verify the information. Citations from peer-reviewed journals or official health guidelines are a good sign.
- Cross-Reference Information: Compare the information with other reputable sources to ensure consistency. If multiple trusted sources agree, the information is more likely to be accurate.
- Avoid Sensationalism: Reliable health information is factual and straightforward. Be cautious of sources that use exaggerated or alarmist language to grab attention.
Some examples of trusted sexual health resources include the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the World Health Organization (WHO), and organizations like Planned Parenthood. These sources provide evidence-based information that you can rely on.
The Impact of Misinformation on Public Health
Misinformation doesn’t just confuse individuals—it can have serious consequences for public health. For example, false claims about vaccines or STDs can lead to vaccine hesitancy, increased stigma, and delayed treatment. By promoting accurate information and debunking myths, we can help protect both individual and community health.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
One of the best ways to combat misinformation is to develop critical thinking skills. Ask yourself questions like: Who is sharing this information? What is their motivation? Are there credible sources to back up these claims? By approaching information with a skeptical yet open mind, you can better separate fact from fiction.
By following these guidelines and relying on trusted sources, you can ensure that the information you use to make decisions about your sexual health is accurate and reliable. Staying informed is one of the most powerful tools you have to protect yourself and others.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does “blue waffle” mean on TikTok?
On TikTok, “blue waffle” is often used as a shock term or meme to reference the infamous internet hoax. Some users may post about it as a joke or to provoke curiosity, but it’s important to remember that blue waffle disease is not a real medical condition.
Are there any pictures of blue waffle disease on Twitter?
While you may come across claims or links to images of “blue waffle disease” on Twitter, these are typically part of the same internet hoax. The original image was heavily edited and not representative of any real medical condition. Always be cautious of graphic content shared online.
Is blue waffle disease mentioned on WebMD?
No, blue waffle disease is not mentioned on WebMD or any other reputable medical website. WebMD provides accurate, evidence-based information about real health conditions, and blue waffle disease is not one of them.
Can men get blue waffle disease?
Since blue waffle disease is not a real condition, it cannot affect anyone, regardless of gender. However, men should still be aware of real STDs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and HPV, which can have serious health consequences if left untreated.
What are the symptoms of real STDs that people confuse with blue waffle disease?
Some symptoms attributed to blue waffle disease, such as unusual discharge, itching, and irritation, are actually symptoms of real STDs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and bacterial vaginosis. If you experience these symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Is blue waffle disease mentioned on Wikipedia?
As of now, there is no Wikipedia page for blue waffle disease because it is not a recognized medical condition. Wikipedia focuses on factual, well-documented topics, and blue waffle disease does not meet those criteria.
What should I do if I see blue waffle disease pictures online?
If you encounter graphic images claiming to show blue waffle disease, it’s best to avoid engaging with them. These images are often fake and designed to shock or mislead. Instead, focus on learning about real STDs and how to protect yourself from them.
Are there any real conditions that cause discoloration in the genital area?
While blue waffle disease is not real, certain medical conditions can cause discoloration or unusual changes in the genital area. For example, poor circulation, bruising, or infections like cellulitis may cause discoloration. If you notice any unusual changes, consult a healthcare provider.
Can blue waffle disease be cured?
Since blue waffle disease is not a real condition, there is no cure. However, real STDs like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis can be treated with antibiotics. Early detection and treatment are crucial for preventing complications.
Are there any real STDs that cause blue discoloration?
No real STD causes the genital area to turn blue. If you notice unusual discoloration, it could be due to bruising, poor circulation, or another medical condition. Consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis.
Conclusion
Blue waffle disease is not a real STD, but the fear and confusion it caused are very real. This hoax serves as a reminder of the dangers of misinformation and the importance of reliable sexual health education. While you don’t need to worry about blue waffle disease, staying informed about real STDs and practicing safe sex are essential steps to protect your health. If you have concerns about your sexual health, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional.