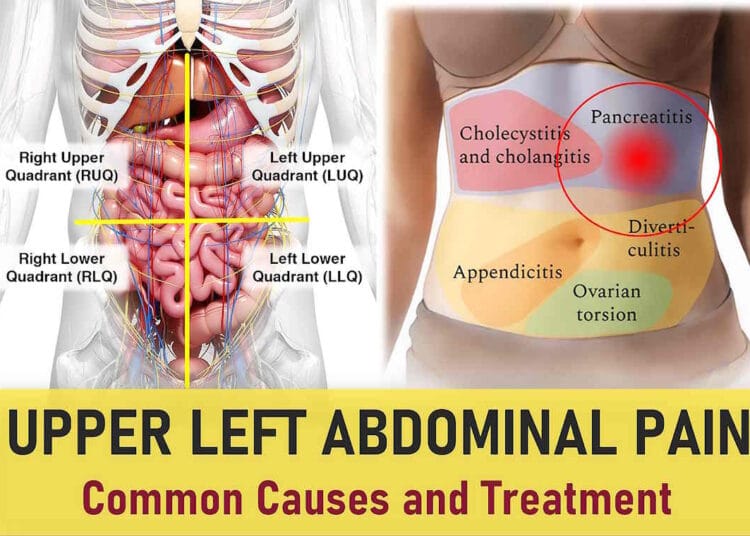
The upper left abdominal quadrant (LUQ) refers to the area on the left side of your abdomen, stretching from the middle line of your chest to the left ribcage and down to the level of your belly button. Pain in this area can range from mild to severe, depending on the underlying cause.
LUQ pain can be related to digestive issues or conditions affecting organs in this region, such as the spleen. Mild issues, like indigestion and constipation, often resolve within a few days. However, more severe conditions, including pneumonia or kidney problems, may require more complex and urgent medical attention.
If left untreated, pain in the left upper quadrant can become debilitating. In some cases, the underlying condition may progress to severe or life-threatening complications. Understanding the potential causes of this pain can help you determine when to seek urgent medical care.

Organs in the Left Upper Abdominal Quadrant?
The left upper quadrant (LUQ) houses several important organs that can contribute to pain in this area. These include:
- Kidney: The left kidney is located in the LUQ, just beneath the ribcage and behind the left lobe of liver. It plays a critical role in eliminating waste from the body and regulating the balance of water, minerals, and salt.
- Spleen: Positioned behind the left ribcage, next to the stomach, the spleen is responsible for filtering blood, regulating blood cell levels, and fighting infections.
- Pancreas: The body and tail of the pancreas are located in the LUQ, near the spleen. This organ produces digestive enzymes and insulin, which helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Stomach: The stomach is a key organ in the digestive system, breaking down food before it moves into the small intestine. The majority of the stomach lies in the LUQ, including the body of the stomach and the cardia, where food enters from the esophagus.
- Adrenal Gland: Located above the kidney, the adrenal gland secretes essential hormones like cortisol and plays a role in regulating water balance, metabolism, and the immune system.
- Left Lung: The left lung, found in the LUQ, is an essential respiratory organ located close to the heart.
- Liver: While most of the liver is situated in the right upper quadrant, the left lobe extends into the LUQ. The liver is involved in digestion, detoxification, metabolism, and immune functions.
- Colon: The transverse section of the colon, part of the large intestine, is located in the LUQ. The splenic flexure, where the colon curves beneath the lower end of the spleen, is also in this region.
- Heart’s Apex: The apex of the heart, located in the center of the chest but leaning slightly to the left, also influences pain in the LUQ. The heart pumps oxygenated blood throughout the body.
What Causes Left Upper Abdominal Pain?
Pain in the LUQ can stem from several causes, with the most common being issues related to the organs in this area. However, it’s important to note that pain in the LUQ can also result from “referred pain,” where discomfort originates from a different part of the body but is felt in the LUQ. This broadens the potential causes of LUQ pain.
Below are some of the most common causes of pain in the LUQ:
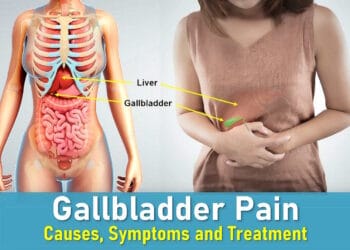
Problems with the Spleen
The spleen is located just behind your stomach, under and behind the left ribs. It has several important functions, including filtering blood, creating blood cells, and storing platelets. Pain related to the spleen can occur for the following reasons:
- Enlargement (Splenomegaly): The spleen can become enlarged due to blood-related cancers like leukemia and lymphoma. This may cause vague, worsening pain. Enlargement of the spleen can also happen during infections like glandular fever.
- Spleen Rupture: A sudden injury, such as a car accident or a heavy fall, can cause the spleen to rupture. This leads to sudden, severe pain shortly after the trauma.
- Sickle Cell Crisis: In individuals with sickle cell disease, a crisis can lead to spleen pain due to blood flow complications.
Problems with the Stomach and Bowels
Many issues related to the stomach and intestines can cause pain in the LUQ. These conditions include:
- Stomach Ulcers: The pain from stomach ulcers can feel like indigestion and may be relieved temporarily by antacids. In severe cases, ulcers can lead to vomiting and may require emergency treatment.
- Indigestion (Dyspepsia): This common issue can cause discomfort in the upper abdomen, often accompanied by heartburn and acid reflux.
- Gastroenteritis: This infection causes crampy pain all over the abdomen, typically along with diarrhea and vomiting.
- Diverticulitis: Inflammation of the pouches in the colon (diverticula) can sometimes cause pain in the LUQ, along with fever and changes in bowel movements.
- Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis: These chronic conditions can lead to widespread abdominal pain, often with loose stools and sometimes blood in the stool.
- Constipation: When the intestines are backed up with stool, discomfort can occur anywhere in the abdomen, including the LUQ. Signs of constipation include infrequent bowel movements and hard stools.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): While IBS typically causes pain lower in the abdomen, it can also lead to bloating and discomfort in the LUQ, often with diarrhea or constipation.
Shingles
Shingles can sometimes cause pain in the LUQ before the rash appears. The pain is typically sharp or burning, and you may feel unwell overall. A few days later, a rash with blisters will appear. The LUQ is a common area for shingles to affect.
Kidney Stones and Infections
Kidney-related issues often cause pain around the left side of the LUQ or in the back (loin), but the pain can spread to the front of the abdomen. A kidney stone or infection can lead to pain along the urinary tract, which could occur anywhere from the lower back (loin) around to the LUQ, and down to below your belly button.
This pain can be quite severe and may be accompanied by other symptoms like fever, pain during urination, or an increased frequency of urination. If you experience these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical attention. Kidney infections and kidney stones are serious conditions, and you should consult with your healthcare provider for a diagnosis and treatment options.
Pain Coming from the Aorta
The aorta is the body’s main blood vessel, responsible for carrying blood from the heart to the rest of the body. It runs down the center of your abdomen, delivering blood to your legs and other parts. In some cases, the aorta can swell, increasing the risk of a leak or rupture. This is known as an aortic aneurysm.
If the aorta develops a leak, you may experience pain in the abdomen that may also radiate to your back. A rare but more severe condition, called an aortic dissection, occurs when the lining of the aorta tears. If the aorta ruptures, it leads to sudden, severe pain in the abdomen, back, or chest, and you may feel very unwell. A suspected aortic issue is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention and treatment.
Pain Coming from the Pancreas
The pancreas is located in the upper part of your abdomen. It produces enzymes that help digest food and hormones like insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels. Inflammation of the pancreas can lead to conditions like acute pancreatitis or chronic pancreatitis, causing upper abdominal pain. This pain may be felt in the LUQ and is typically accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
In acute pancreatitis, fever is also common, and the person may feel very unwell. Additionally, pancreatic cancers can cause upper abdominal pain, though they may not lead to noticeable symptoms until the cancer has progressed to a more advanced stage.
What Are the Other Possible Causes?
Aside from the conditions described above, several other issues can cause pain in the LUQ. This list is not exhaustive but highlights some of the key conditions to be aware of:
Problems with Your Heart
Because the heart is located near the LUQ, certain heart-related conditions can sometimes manifest as LUQ pain. These conditions include a heart attack (myocardial infarction), angina, or pericarditis. If you suspect you are having a heart attack, it is crucial to seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Problems with Your Lungs
If there is an infection or issue affecting the lower part of your left lung or diaphragm, it can lead to pain in the LUQ. Conditions like pneumonia or pleurisy can cause this type of discomfort.
Problems in Your Spine or Back
Pain originating from your spine or back can sometimes radiate to the front of your abdomen. This is referred to as “referred pain” and can be caused by conditions affecting the back or spinal cord.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
In individuals with type 1 diabetes, a serious complication called diabetic ketoacidosis can cause general malaise and sometimes abdominal pain. DKA is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment.
Addisonian Crisis
An Addisonian crisis, which is a complication of Addison’s disease, can also cause significant abdominal pain. This condition is accompanied by other symptoms like fatigue, low blood pressure, and electrolyte imbalances.
Acute Porphyria
Acute porphyria is a rare blood disorder that can cause abdominal pain along with other symptoms like nausea and vomiting.
Pain Referred from the Pelvis
Conditions affecting the pelvic region can sometimes cause pain in the LUQ. Examples include pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or ovarian cysts. In these cases, the LUQ pain is typically accompanied by other symptoms related to the condition.
Muscle Sprains
Muscle sprains, particularly those that occur after unusual physical activity, can also cause discomfort in the LUQ. If the pain is related to a muscle strain, moving the affected muscle may worsen the pain. On the other hand, remaining still may alleviate the discomfort.
What Causes Left Upper Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy?
While any of the conditions mentioned above can cause LUQ pain during pregnancy, it’s essential to consider some pregnancy-specific causes. In early pregnancy, one of the primary concerns is ectopic pregnancy, which can cause pain in the abdominal area.
During pregnancy, it is common for the growing uterus to press on other organs, including the stomach and diaphragm, leading to discomfort. Indigestion, which often results from this pressure, is also a common issue during pregnancy. Additionally, urinary tract infections (UTIs) are more prevalent in pregnant individuals and can contribute to LUQ pain.
What Causes Left Upper Abdominal Pain in Children?
In young children, pinpointing the exact location of pain can be challenging, which can lead to a wide range of potential causes. Common causes of LUQ pain in children include:
- Constipation: Difficulty passing stool can cause discomfort in the abdominal region.
- Anxiety: Emotional distress can sometimes manifest as physical pain in children.
- Gastroenteritis: Infections in the stomach or intestines often lead to abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Mesenteric Adenitis: In viral infections like colds, lymph nodes in the abdomen can become inflamed, causing pain.
- Appendicitis: Although this usually causes pain in the lower right abdomen, if a child cannot pinpoint the pain or if the appendix ruptures, LUQ pain may also occur.
- Pneumonia: Infections in the lower lungs can cause pain that radiates to the abdominal region.
Additionally, many of the adult causes mentioned earlier may also lead to LUQ pain in children.
Are Everybody’s Organs in the Same Place?
Very rarely, some individuals have their organs arranged in the opposite direction to the typical arrangement. This condition, called situs inversus, occurs in fewer than 1 in 10,000 people. If you have situs inversus, conditions affecting the right upper quadrant (RUQ) could cause pain in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) instead.
Should I See a Doctor for Upper Left Abdominal Pain?
Yes, if your pain persists, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. Seek immediate medical attention if:
- Your pain is severe.
- You have recently lost weight without trying or have lost your appetite.
- You are vomiting blood or notice blood in your stool (including very dark stools, which may indicate old blood higher in the gut).
- You have a high fever with shaking (rigors).
- You are experiencing shortness of breath.
- You have difficulty swallowing, or feel that food is getting stuck in your food pipe (esophagus), or experience pain in your lower throat or chest when swallowing.
How is Left Upper Quadrant Pain Diagnosed?
Your doctor will begin by talking with you and conducting a physical examination. In many cases, they may be able to identify the cause based on your symptoms. For instance, if the typical rash of shingles is present, no further testing may be necessary.
The doctor will likely palpate your abdomen, especially the area where you are feeling pain, but may also examine other parts of your body, including your chest. To rule out kidney problems, a urine sample may be required. Further tests could include:
- Blood tests to evaluate organ function, check for inflammation, or detect infection.
- A pregnancy test if there is any possibility of pregnancy.
- A stool sample to test for stomach infections.
What Are the Next Steps?
The next steps depend on the findings during your examination. In some cases, no further tests may be needed. For example, if the doctor suspects indigestion, constipation, or shingles, additional testing might not be necessary.
If a heart or lung issue is suspected, tests like an electrocardiogram (ECG) or chest X-ray might be required. If a problem with the stomach or upper intestines is suspected, an endoscopy may be performed, where a tube with a camera is inserted into the stomach for a closer look.
In some cases, imaging tests like a computed tomography (CT) scan or ultrasound may be used to examine the spleen, pancreas, or kidneys. Additional procedures may include colonoscopy, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
Not everyone will require all these tests, and some people may not need any at all.
Treatment for Upper Left Abdominal Pain
Upper left abdominal pain (LUQ pain) can arise from numerous causes, ranging from digestive issues to more serious organ-related conditions. Addressing this pain requires a tailored approach based on the underlying cause. Below, we outline treatments aligned with specific causes, home care tips, preventive measures, and when to seek medical attention.
Specific Causes and Corresponding Treatments
1. Spleen Problems
- Enlarged Spleen (Splenomegaly): Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause, such as infections or blood disorders, often with medications or other targeted therapies.
- Spleen Rupture: This medical emergency requires immediate surgical intervention.
- Sickle Cell Crisis: Pain management, hydration, and oxygen therapy are typical treatments. Some cases may require blood transfusions.
2. Stomach and Bowel Issues
- Stomach Ulcers: Antacids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and antibiotics (for H. pylori infections) are commonly used. Severe cases may need surgical repair.
- Indigestion: Lifestyle changes, antacids, and dietary modifications can provide relief.
- Gastroenteritis: Focus on hydration, rest, and, in severe cases, antibiotics (for bacterial infections).
- Diverticulitis: Antibiotics, a liquid diet, and rest help during flare-ups. Surgery may be needed for complications.
- Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, or biologics are commonly prescribed. Dietary adjustments are crucial.
- Constipation: Increased fiber intake, hydration, and laxatives can help.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Treatment involves dietary management, stress reduction, and symptom-specific medications.
3. Kidney Stones and Infections
- Kidney Stones: Pain relievers, increased fluid intake, and sometimes lithotripsy (shock wave therapy) to break down large stones.
- Kidney Infections: Antibiotics and hospitalization for severe cases.
4. Pancreas Problems
- Acute Pancreatitis: Treatment involves fasting, IV fluids, and pain relief. Severe cases may require hospitalization.
- Chronic Pancreatitis: Pancreatic enzyme supplements and dietary modifications are standard approaches.
- Pancreatic Cancer: Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
5. Heart and Lung Conditions
- Heart Problems (e.g., angina, heart attack): Emergency care with medications, angioplasty, or surgery as needed.
- Lung Issues (e.g., pneumonia, pleurisy): Antibiotics for infections, anti-inflammatory medications, and supportive care like oxygen therapy.
6. Other Causes
- Shingles: Antiviral medications, pain relievers, and topical treatments for the rash.
- Aortic Aneurysm or Dissection: Emergency surgery or vascular repair is often required.
- Muscle Strain: Rest, ice application, and pain relievers can help alleviate symptoms.
Home Care Remedies
For mild or temporary LUQ pain, consider these home remedies:
- Apply a warm compress to relax muscles and ease pain.
- Stay hydrated and drink clear fluids like water or herbal teas.
- Eat small, bland meals such as rice, bananas, and toast.
- Avoid spicy, greasy, or acidic foods that may irritate the stomach.
- Rest and avoid strenuous activities.
Preventive Measures
Proactively reducing the risk of LUQ pain involves maintaining overall health:
- Follow a balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables.
- Stay hydrated by drinking at least 8 glasses of water daily.
- Exercise regularly to enhance digestion and general health.
- Limit alcohol consumption and avoid smoking.
- Address underlying chronic conditions with regular medical follow-ups.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical care if you experience any of the following:
- Sudden, severe, or worsening pain.
- Pain accompanied by fever, chills, or vomiting.
- Blood in vomit, stool, or urine.
- Unexplained weight loss or loss of appetite.
- Difficulty breathing or chest pain radiating to the LUQ.
- Persistent pain lasting longer than a week despite home care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the most common causes of left upper abdomen pain?
Some common causes of LUQ pain include digestive issues like indigestion, stomach ulcers, and gastroenteritis, as well as problems with the spleen, kidney, or pancreas. Pain can also be referred from other parts of the body, such as the heart or lungs.
How can I tell if my left upper abdomen pain is serious?
If you experience severe pain, fever, vomiting blood, or difficulty swallowing, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention. These symptoms may indicate a serious condition like a ruptured spleen, heart attack, or gastrointestinal bleeding.
Can LUQ pain be a symptom of a heart problem?
Yes, the heart is located near the LUQ, and conditions like heart attacks, angina, or pericarditis can present with pain in this area. If you suspect a heart issue, seek medical help immediately.
What should I do if I have persistent LUQ pain?
If your LUQ pain does not improve or worsens, it is important to see a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. The underlying cause of the pain must be identified and treated appropriately.
How is left upper quadrant pain diagnosed?
Your doctor will perform a physical examination and may request tests such as blood work, urine tests, imaging scans (like CT scans or ultrasounds), or endoscopy to determine the cause of the pain.
Conclusion
Left upper quadrant pain can be caused by a wide range of conditions, from mild issues like indigestion to more serious problems involving organs such as the spleen, kidney, pancreas, and heart. It is important to listen to your body and seek medical attention if the pain is severe or accompanied by other concerning symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and ensure a quicker recovery. If you experience persistent or worsening pain, consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and appropriate care.